UTIs, or urinary tract infections, refer to an infection that occurs along the urinary tract. In men, the urinary tract consists of the kidneys, ureter, bladder, prostate and urethra. The testes although not strictly along the urinary tract can also be infected and is considered as UTI.
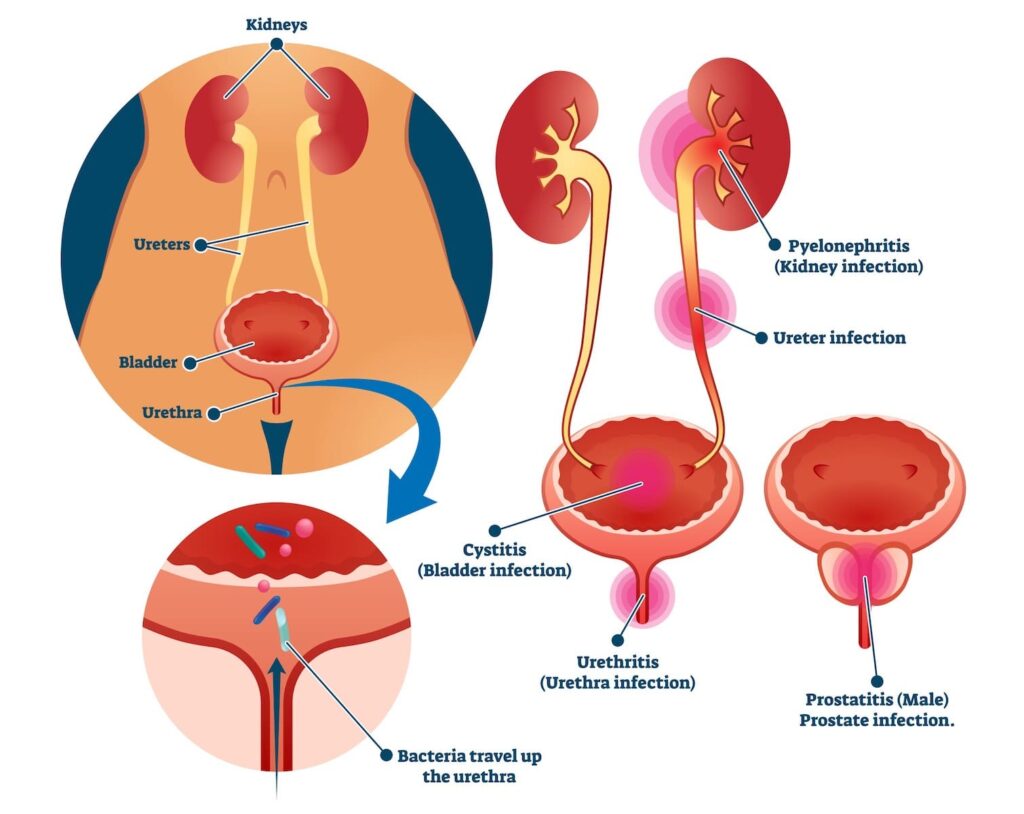
Contrary to popular belief, men can get UTIs too. UTIs tend to be more common in women because the urethra in women is shorter, which allows the bacteria to move through the urinary tract easier and access the bladder. Conversely, men have longer urethras, therefore lowering their overall risk of getting UTIs.
Although uncommon, UTIs still occur in men. Studies show that over 12% of men experience urinary symptoms linked to a UTI in their lifetime.
There are several causes of UTIs among men. In young men, sexually transmitted infections are a common cause of UTIs, along with recent urological surgeries and procedures. Men with congenital abnormalities of the urinary tract are also at higher risk of UTIs.
In older men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), the obstruction of urine flow can predispose them to the development of UTIs. Men with medical conditions such as diabetes may also be at higher risk of UTIs as sugar levels in urine are conducive to bacteria growth. Other conditions that predispose a man to UTIs include having a weakened bladder due to old age or previous spinal cord injuries leading to incomplete bladder emptying.
Kidney stones are also known to cause UTIs, especially when they are causing obstruction to urine flow.
UTIs often go away on their own, especially in mild infections.
These symptoms may subside as the infection resolves. It is important to note that although some people especially older females may have bacteria in their urine but may not experience any symptoms at all, and this does not constitute a UTI.
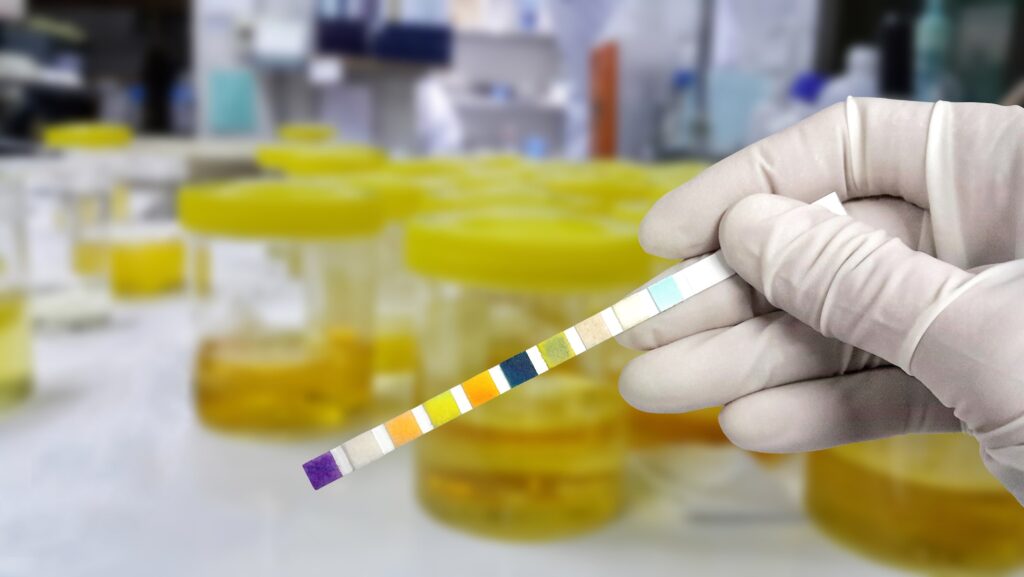
UTIs are diagnosed by the detection of bacteria in urine samples (urinalysis) of a symptomatic person. This is done by obtaining a urine sample from the patient and sending it off to a lab for bacterial culture. Following the identification of the bacteria, antibiotics that target the particular bug will then be prescribed to treat the UTI.
At times, UTIs can go away on their own. However, experiencing severe symptoms (pain in your back, nausea, chills, vomiting) may require a visit to your doctor or urologist. Prompt treatment of UTIs is important to prevent the infection from spreading upwards to areas such as the kidney or blood stream, which can result in more complications.
UTIs are generally treated with antibiotics, either in tablet form or via an intravenous drip for more severe infections. Patients may also be given medication like panadol to help alleviate symptoms like fever and pain.
After recovery, you will also be counselled on lifestyle measures to help reduce your risk of reinfection. These include drinking enough water, maintaining good hygiene of the lower perineal area, and controlling your medical comorbidities, such as diabetes.
Although urinary tract infections occur less often in men, they can still happen and requires evaluation by a urologist to rule out any underlying causes. Treating a UTI can be as easy as drinking more water and keeping good hygiene practices. However, it is important to seek medical attention early to prevent complications such as worsening infection and scarring to the urinary tract. Staying hydrated, maintaining good hygiene of the genital areas, and living a healthy lifestyle will all be helpful in reducing your overall risk for UTIs.
If you experience any of the aforementioned UTI symptoms, please visit a Urologist. Here at Assure Urology & Robotic Centre, Dr Terence Lim will work with you in creating a treatment plan that best suits you.
No issue is too small. Contact any of our friendly staff and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
Reach out to us for expert urological care.
For enquiries, leave a message and our friendly team will get in touch with you.
For urgent enquiries after office hours, call or WhatsApp us at (65) 9835 0668.
Monday – Friday: 9:00AM – 5:00PM
Saturday: 9:00AM – 12:30PM
Sunday & Public Holiday: CLOSED
Reach out to us for expert urological care.
For enquiries, leave a message and our friendly team will get in touch with you.
For urgent enquiries after office hours, call or WhatsApp us at (65) 8082 1366.
Monday – Friday: 9:00AM – 1:00PM | 2:00PM – 5:00PM
Weekends & Public Holidays: CLOSED

© 2023 All Rights Reserved | Assure Urology & Robotic Centre | Terms & Conditions